Copyright © 2025 Jaipur Tuff. All rights reserved.
Laminated glass provides higher mechanical resistance and security benefits.
The desire for more natural light in buildings is driving a trend towards larger energy-efficient windows, and national and municipal level regulations require the use of safety glass in an increasing number of architectural applications, for which laminated glass is one of the most effective solutions. A greater demand for noise reduction in both residential and commercial builds, gives rise to increased use of acoustic laminated glass.
Laminated glass is two or more lites of glass permanently bonded together with one or more polymer interlayers using heat and pressure. The glass and interlayers are available in a variety of colors and thicknesses which provide the desired appearance and performance to meet the relevant building code standards and customer requirements.
While float glass provides an excellent base product, laminating the glass can add other properties and benefits such as safety and security, sound control, UV protection, and color. Laminated glass products make float glass suitable for today’s demanding architectural applications such as: noise reduction, blast mitigation, forced entry, protection from broken glass – or a combination of these.
Laminated glazing can be adapted to suit many architectural projects, particularly those that require demanding performance in terms of increased safety, security (impact resistant glass), UV protection, noise reduction or a combination of these – while strongly considering the aesthetics, architects desire.
Glass is often laminated to protect people from glass breakage. Laminated safety glass can be used in many different ways to provide increased safety and security.
Under sufficient impact force, laminated glass will break. Glass fragments tend to adhere to the plastic interlayer and remain largely intact, reducing the risk of injury. This is particularly important when there is a risk of broken glass falling from high-rise buildings, or from overhead applications such as roof glazing, canopies and skylights. In hurricane-resistant applications, the glass can help prevent water and air from entering the building.
Laminated glass is considered as “safety glass” when it meets the requirements of the various code organizations that set standards for safety.
Acoustic laminated glass adds noise reduction to other benefits of laminated glass, helping to reduce noise levels so that people can be more comfortable in their living and work spaces.
The acoustic performance of glazing is expressed using the weighted sound reduction index Rw, expressed in decibel (dB). In the final acoustic estimation, other two factors are included:
Specificly designed acoustic interlayers reduce vibrations and significantly improve the sound insulation compared to float glass or even standard laminated glass.
Heat strengthened and tempered glass can be incorporated into laminated glass units to further strengthen the impact resistance. This type of laminated glass is often specified for applications where anti-intrusion or forced-entry security are concerns, ballistic and blast mitigation, and hail protection.
When architects require plenty of natural daylight to enter a building without damaging interior furnishings and fittings – laminated glass can absorb up to 99% of the damaging UV rays which can be responsible for up to 50% of fading This protection means that interior surfaces and furniture are likely to last longer.
Every glass project is unique and so the desired color, light transmission and privacy varies. Using laminated glass for a project doesn’t mean you have to sacrifice on its appearance. Laminated glass offers a wide range of colored PVB interlayer options, which can be combined or used separately, resulting in a choice of over 3,000 transparent, translucent or opaque color options.
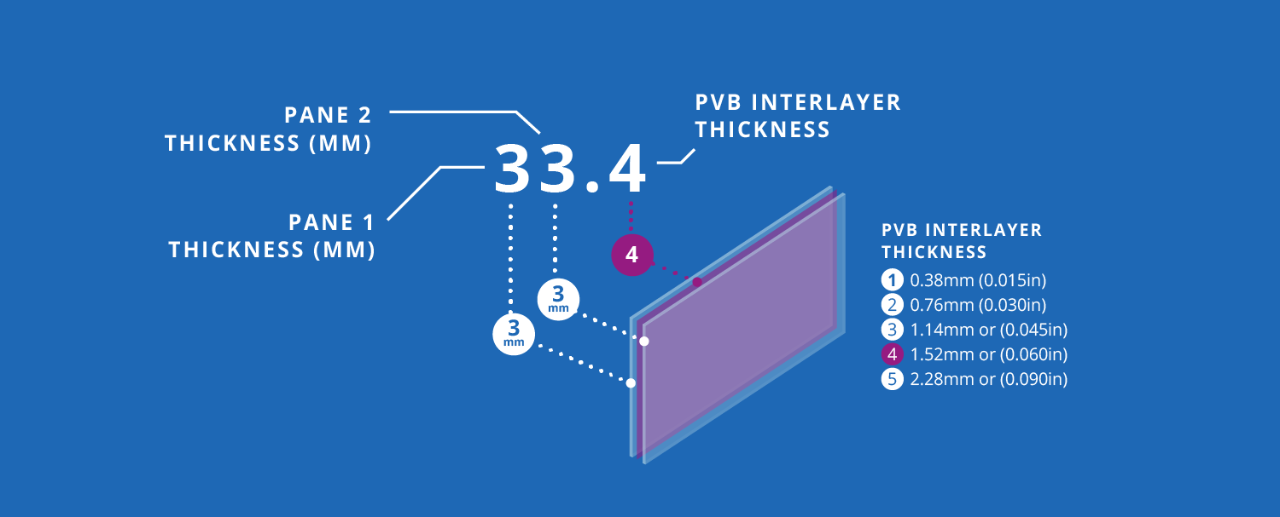
The nomenclature for laminated glass describes its build-up by considering the number and thickness of the glass panes used and the thickness of the interlayers.
Example: Laminated glass 33.4

Premier organization renowned for its exceptional expertise and outstanding achievements in the field of manufacturing industrial glass.
Copyright © 2025 Jaipur Tuff. All rights reserved.